Rosacea
Rosacea is an inflammatory dermatosis associated with the sebaceous follicle and is characterized by the appearance of erythema, telangiectasias, inflammatory lesions, and edema with alternating periods of exacerbation and remission.
It is usually located on the face.

01. History & examination
We begin by taking a history from the patient and examining for uniformity or inhomogeneity.
02. Treatment & management
We prioritize modern therapeutic methods based on our patient's choices and desires.

03. Emphasis on the result
We are by your side at every stage to help you with personalized treatments to have healthy and beautiful skin.
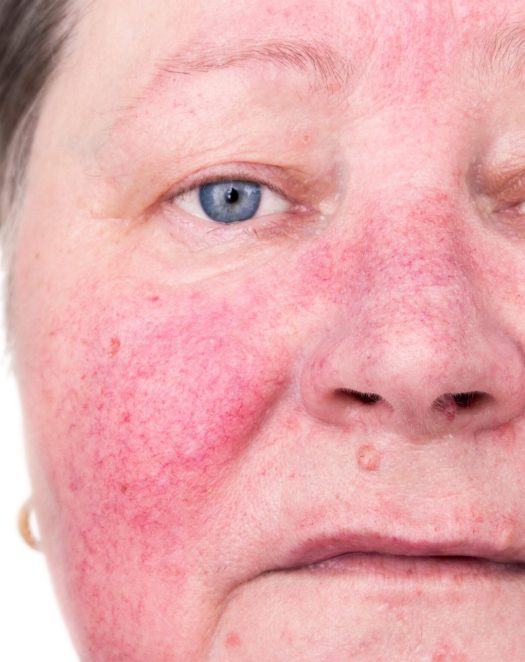
Your skin health is our priority
Treatment options depend on the stage and severity of the disease.
In the initial stages, the local application of vasoconstrictive cosmetic preparations, often of plant origin, is recommended. In more advanced stages, the use of local pharmaceutical preparations containing mainly metronidazole or azelaic acid is required. In advanced stages (papillopustular), oral medication is necessary, either antibiotics (tetracyclines) or vitamin A derivatives (isotretinoin) in low doses. In the final stage of rhinophyma, dermatosurgical intervention is required with cauterization of the lesions with diathermy or laser.
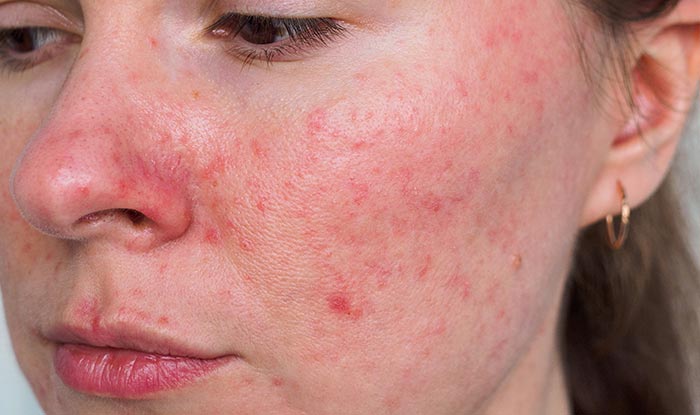
The disease is characterized by 4 stages:
- Transient erythema:Patients complain that either suddenly or after the influence of a triggering factor such as increased ambient temperature, consumption of alcohol or spices, and especially mental stress, they experience transient erythema (redness), mainly on the face, neck, or sternum.
- Permanent erythema: The redness is now permanent on the face, while small blood vessels begin to appear on the surface of the skin, especially on the sides of the nose and cheeks. The redness becomes even more intense with the influence of triggering factors.
- Papillomas: In addition to the erythema, red pimples (papules) also appear on the skin, some of which contain pus (pustules). The picture resembles common acne of adolescence, but the main characteristic of the latter is missing, the comedones (small black spots (open comedones) or whitish plaques (closed comedones).
• In the last stage, which fortunately is rare, in addition to all the previous characteristics, it also occurs intense hyperplasia of the sebaceous glands along with overgrowth of connective tissue, resulting in thickening of the skin and facial deformity. Depending on the location of the lesion, it is distinguished into rhinophyma (on the nose), frontal phyma, ear phyma and cheek phyma.
CAUSES
The etiology is actually unknown but several possible factors have been blamed, including:
• Gastrointestinal disorders
• Microorganism activity
• Vascular disorders
• Abnormality of the pilosebaceous unit
• Damage to underlying tissues
• Genetic predisposition
• Combination of genetic predisposition and sun exposure
• Pharmaceutical treatments that cause vasodilation
The Result of Our Work
by experienced masters of our clinic.
Frequently asked questions
Contact us
We are here for you for any questions or problems you may have! We will be happy to serve you!

Phone:
2441 025155
Address:
14 Vassiardani, Karditsa
E-mail:
info@makrisderma.gr
Online Appointment
